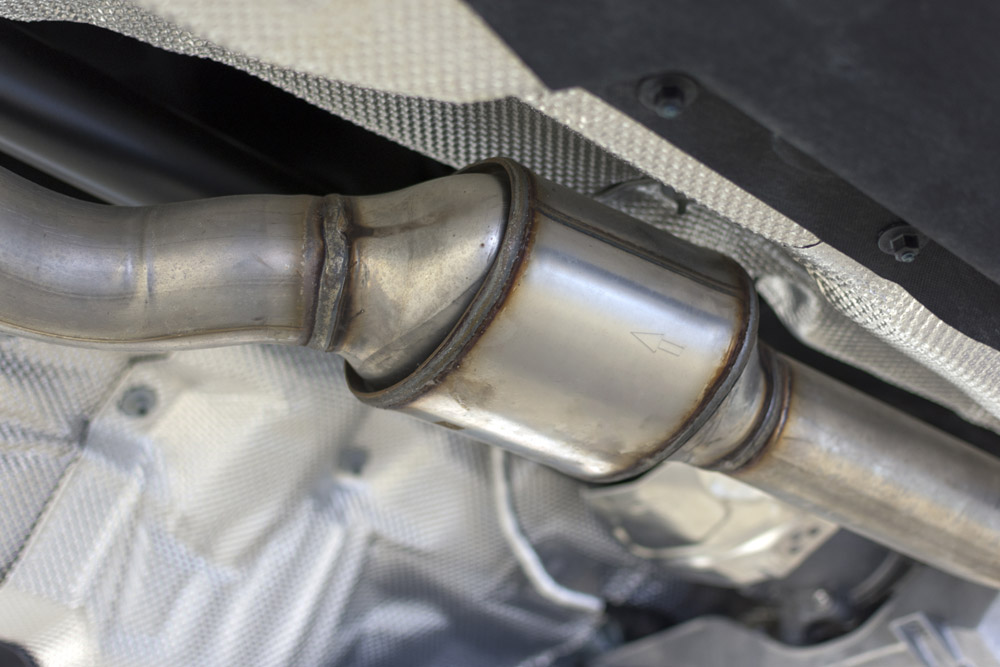
Do you know what a catalytic converter is, and what it does? Learn more about it from the Clearfield car repair team at Master Muffler.
If you think it’s hard work getting your car emissions tested every year before your registration expires, think about how hard your catalytic converter works daily to remove the most harmful compounds from your car’s exhaust.
What’s in a Car’s Exhaust?
When an engine uses fuel, it produces emissions that contain a variety of elements. Some are better for the environment than others, which is why emissions have been regulated since the 1970s.
Gasoline engine emissions can include the following:
- Nitrogen gas (N2)
- Water (H2O)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
- Sulfur oxides
- Hydrocarbons
- Carbon particles (particulate matter)
- Volatile organic compounds (VOC)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
How a Catalytic Converter Works
The catalytic converter performs two main functions for your vehicle:
- Reduction
- Oxidation
Reduction is the process of reducing the amount of nitrogen and nitrogen oxide from your vehicle’s emissions. Removing oxygen from these compounds is the goal.
Oxidation is the process of combining elements to reduce the amount of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide in your vehicle’s emissions.
Both of these processes are necessary to remove the harmful compounds in emissions, or at least significantly reduce them. This makes the air we breathe safer, and helps prevent overwhelming amounts of pollution, especially in big cities.
So, how does a catalytic converter perform this work in your vehicle?
Elements of a Catalytic Converter
The parts of the converter work together to create chemical changes in the exhaust fumes. Metal, ceramic, and noble metals provide an environment for harmful elements to transform.
- Metal casing
- Ceramic honeycomb
- Platinum
- Palladium
- Rhodium
- Oxygen sensor
When exhaust fumes travel through the vehicle’s exhaust system, they pass through the catalytic converter. Nitrogen oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons react with the noble metals in the ceramic honeycomb and convert them to carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen gas.
The converter includes an oxygen sensor so the chemical reactions are balanced with the right amount of oxygen. As you probably know, fuel combustion also involves oxygen, so a sensor is necessary to ensure the systems are supplied properly for efficient function. If the catalytic converter fails, get in touch with your local Clearfield car repair team because it’s a problem that can’t be ignored.
Why a Honeycomb?
Bees are pretty smart, and the honeycomb shape and structure is an inspiration for engineers everywhere. The advantage of a honeycomb shape in the converter is that it provides a large amount of surface area without taking up a lot of space in your exhaust system. As the fumes pass through the ceramic honeycomb, they get a lot of exposure to the precious metals coating the honeycomb so the harmful elements can be converted. Additionally, honeycomb is a strong shape and can withstand stress.
Problems with Precious Metals
While precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium are necessary for the conversion process, they cause potential problems. With them being so valuable, it’s tempting for thieves to cut catalytic converters out from underneath vehicles. The precious metals can be scrapped for big sums of money, and you are left with an expensive car repair as a result.
The Effectiveness of Catalytic Converters
Did you know the original catalytic converters needed up to 15 minutes to warm up? This meant they weren’t doing any conversion work until the vehicle had been driving for quite a while, allowing harmful pollutants to be emitted. Thankfully, today’s converters only need a couple of minutes before they’re heated up and ready to go. The higher the temperature, the more efficiently the catalytic converter can work.
- 275 degrees = about 50% efficiency
- 500 degrees = closer to 90% efficiency
Under ideal conditions, a catalytic converter reduces at least 90% of harmful emissions from a vehicle’s exhaust.
Catalytic Converters and Diesel Engines
A diesel-powered engine does rely on a catalytic converter to reduce toxic emissions, but there are some differences.
A diesel engine uses a two-way oxidation catalyst to remove carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons from exhaust. There is no reduction process needed for a diesel vehicle. Without the reduction process occurring in a converter, the exhaust from a diesel does tend to have higher levels of nitrogen oxides compared to a gasoline engine.
Diesel engines produce soot or particulate matter. As a result, the exhaust system implemented filtration to remove those particles from the exhaust and prevent all of them from entering the atmosphere.
Another difference in the conversion process is the size of the engine. A diesel engine is typically larger than a gasoline engine. So it’s common to have more than one catalytic converter on a diesel vehicle in order to handle the exhaust volume.
If you’re looking for Clearfield car repair experts, look no further than Master Muffler. For any issues in your exhaust system, including the catalytic converter, we’re here to help.
Related Posts
Key Takeaways On average, passenger vehicle tires last 40,000 to 60,000 miles, depending on type, driving habits, and maintenance. Replace tires when tread depth reaches 2/32”, if damaged, or older than 10 years. Regular rotation, alignment, and proper inflation extend tire life. Aggressive driving, poor roads, and harsh weather shorten tire lifespan. Take advantage [...]
When you think about car maintenance, you probably focus on oil changes, tire rotations, and maybe even brake pad replacement. But what about your brake fluid? If you’ve ever wondered, “What does brake fluid do?” or “Why is brake fluid important?”, you’re not alone. Brake fluid might not be the most talked-about part of [...]
Is that high-pitched squeal from your brakes driving you—and everyone else—crazy? Don’t ignore it. Squeaky brakes aren’t just annoying, they’re your car’s way of saying something needs attention. Whether you're cruising through Salt Lake City or winding up Idaho’s mountain passes, here’s what’s likely going on, how you can fix it, and when it [...]