The Salt Lake City car repair technicians at Master Muffler make it easy to get to know your car from top to bottom, inside and out.
Did you know that even some electric vehicles make use of internal combustion engines? It’s not just a process found in gasoline and diesel engines. However, we’ll focus on fuel-powered internal combustion engines for this article.
The Chemistry of an Internal Combustion Engine
Combustion means burning. It’s the chemical process of mixing fuel (gasoline, diesel, etc…) with air and using thermal energy to get other parts of the engine moving. This is why internal combustion engines (ICE) are sometimes referred to as heat engines. Essentially, an internal combustion engine is converting thermal energy into mechanical energy.
Internal Combustion Engine Components:
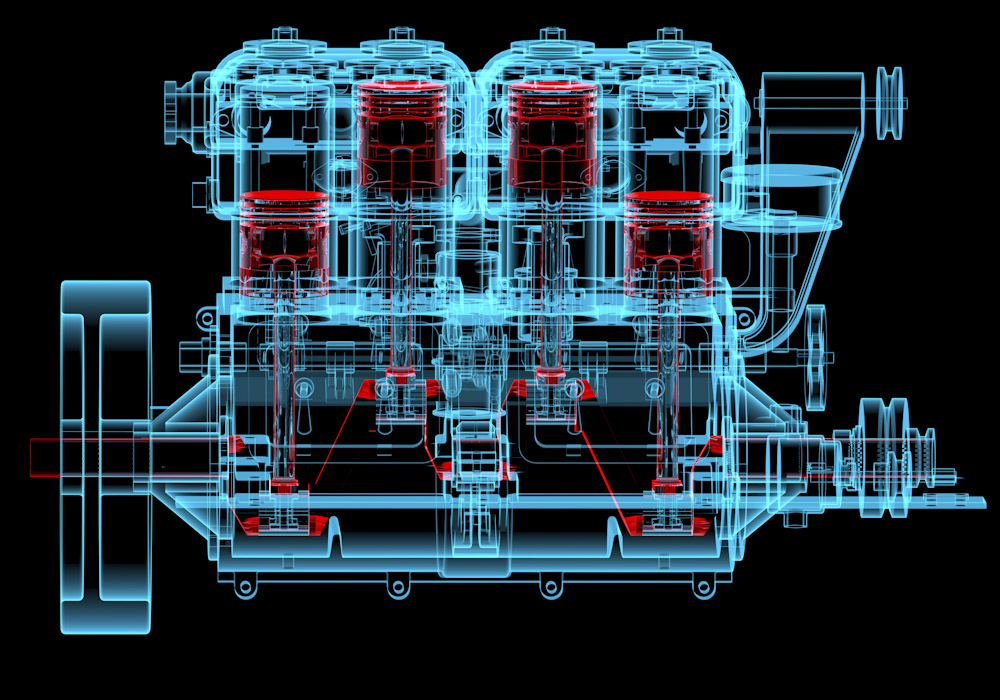
There are a lot of fixed and moving parts of your engine. Here’s a rundown of what’s involved in internal combustion engines with a four-stroke cycle.
- Exhaust camshaft
- Exhaust valve bucket
- Spark plugs
- Intake valve bucket
- Intake camshaft
- Exhaust valve
- Intake valve
- Fixed cylinders
- Each cylinder contains a camshaft, valves, valve buckets, spark plugs, and injectors.
- Pistons
- As gasoline expands, the piston moves up and down in the cylinder.
- Engine block
- This houses the piston, a connecting rod, and the crankshaft. Coolant flows through the engine block to regulate the temperature.
- Crankshaft
- This rotates as the piston moves through the power stroke, making the wheels of the car move.
With all these engine components, you can see why it’s important to follow a regular car repair schedule; you don’t want to end up with a bigger problem by neglecting a small one early on.
Four-Stroke Cycle Engines
We mentioned that all of this happens in a four-stroke internal combustion engine. But what does that mean?
“Four-stroke” refers to how many times a piston moves to turn the crankshaft two full rotations, or 720 degrees. A piston will “pump” four times to complete the process of converting thermal energy into mechanical energy. Three of the four strokes are consuming energy, while only the power stroke produces torque/movement.
Steps completed in a piston stroke:
- Intake
- Compression
- Combustion and power stroke
- Exhaust
Types of Internal Combustion Engines
There are two kinds of internal combustion engines primarily in use in vehicles today.
- Spark ignition (for gasoline-powered vehicles)
- Compression ignition (for diesel-powered vehicles)
Master Muffler’s Salt Lake City car repair experts offer services for either type of combustion engine.
Spark Ignition Process
If you drive a gasoline-fueled car, here’s how the spark ignition process works.
- During the intake process, a valve at the top of a cylinder opens to draw in a fuel and air mixture.
- In the cylinder, the piston then compresses this mixture of fuel and air, at which time a spark ignites it. The intake and exhaust valves are closed at this time, forcing compression.
- Once the spark initiates combustion, the gases push the piston in the power stroke.
- The power stroke occurs with both intake and exhaust valves still closed; the pressure in the cylinder increases, continuing to push the piston down. It is during this stroke that the engine produces energy.
- During the exhaust stroke, the exhaust valve opens. The exhaust is vented out of the cylinder to the exhaust system pipes. During this part of the process, the engine uses the energy produced (i.e. the crankshaft is rotated with the energy created during the power stroke).
Compression Ignition Process
- At intake, air, without fuel, is inducted into the engine cylinders.
- The air is compressed by the piston, and then the diesel fuel is added. This causes ignition and the mechanical energy needed to turn the crankshaft.
- As with a gas engine, the diesel engine then vents exhaust gases.
A diesel engine completes this process a bit more efficiently than a gas engine; it can do all this work and get you about 20% more from the same amount of fuel.
Maintaining Your Internal Combustion Engine
Did you know that when an engine hits 100,000 miles, it has powered over 300 million revolutions? That’s a lot of work from your pistons, and with routine maintenance, you can continue hitting the road for miles to come. Our Salt Lake City car repair team recommends the following routine maintenance for optimal engine performance.
- Stick to your regular oil change schedule to keep cylinders running smoothly. Going too long between changes creates buildup, making it difficult for all the moving parts to do just that- move!
- Change the fuel filter regularly. An engine needs air to function, so make sure the air being inducted is clean.
- Use the right octane fuel for your car. Your owner’s manual suggests which octane to use, and you should stick with it. Your engine has been tested to show which octane rating performs most efficiently, meaning what type of fuel combusts at the precise moment it’s meant to. If your engine has a high compression ratio, you’ll need higher octane fuel.
- Octane Ratings for Gasoline
- 85: designed for use in high-elevation areas of the US, and vehicles with carbureted engines
- 87: regular
- 88-90: midgrade
- 91-94: premium
- Octane Ratings for Gasoline
Don’t wait until your check engine light illuminates to schedule routine maintenance. Troubleshooting car repair needs is a lot easier before the problem gets too big. If you suspect you have an issue, give us a call or pay us a visit. We are always happy to help.
Related Posts
As an EV owner, understanding your vehicle's battery is critical. From its capacity to its lifespan, and everything in between, we'll guide you through what you need to know to optimize your EV experience. So buckle up and get ready - we're about to shed some light on the electrifying world of EV batteries. What [...]
If your car is running hot, it can be a sign that something’s not right with your engine. Fortunately, diagnosing the cause of an overheating engine isn't too difficult if you know what to look for and how to address it. Keep reading if you want to learn the most common issues that occur when [...]
Your vehicle's exhaust system serves a critical role in managing the byproducts of the combustion process and ensuring optimal engine performance. The appearance of colored smoke from the exhaust pipe, either when stationary or accelerating, can provide valuable clues to underlying mechanical issues. What is a car exhaust? A car exhaust is a system [...]